Why and when should remote maintenance be considered at all? The main reasons for using a remote maintenance solution are the constant increase in digitization and the growing networking of products and services. From an economic point of view, there is also a need for an effective, global use of resources, and remote maintenance is an ideal tool in this context. A core consideration here are the regulatory requirements that a remote maintenance solution must meet to make it safe and secure. Before employing any remote maintenance solutions, it is important to not only consider the security risks, but also the positive economic aspects, in other words: weighing up the risks and benefits. Many advantages of remote maintenance – which we will examine in more detail – are obvious: For example, remote maintenance of process plants via public networks in an industrial environment provides users with considerable cost advantages. On the other hand, the associated risks must be adequately controlled in view of the possible consequences. If an industrial user’s production facilities do not have an effective protective shield, a single security gap makes production processes vulnerable to attacks – with potentially serious outcome. A vulnerability in a process network can lead to a possible reduction in security and protection and thus to an increased risk of environmental and economic damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Remote Maintenance Solutions
The next step is to compare the advantages and disadvantages of a remote maintenance solution against this backdrop. First, let’s look at the advantages: Remote maintenance can significantly minimize service costs and improve response times. At the same time, plant availability can be increased due to shortened downtimes. The high flexibility of remote maintenance leads to optimal monitoring, configuration and control of the system, with complete control over system access from any location and at any time. Every interaction can be monitored and recorded in real time. Ultimately, there are considerable cost advantages associated with remote maintenance of process plants via public networks.
Possible disadvantages include a key issue: A solution that does not meet the highest safety and security requirements can make the production process vulnerable to attacks. In fact, only very few solutions available on the market meet the regulatory requirements, such as those specified by the German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI). At the same time, the constantly changing and increasing threat situation is placing significantly higher demands on security.
When introducing remote maintenance solutions, considerable know-how is required to manage the primary problem of security risks efficiently. Ideally, this safety and security know-how is already available in your own company, alternatively, cooperation with a trustworthy partner can provide the necessary expertise.
Remote Access Meets Smart Safety Platform
A functional concept that meets all safety and security requirements must be seamless, without any gaps. From the user’s perspective, it makes sense to use a comprehensive security environment from a single source. HIMA has taken up this challenge and combined the know-how of the IT-security specialists from genua with its own safety expertise. The result is a highly secure remote access solution that complements the previously presented HIMA Smart Safety Platform (SSP) concept
What Should a Remote Maintenance Solution Be Able to Do Today?
The German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI), the central point of contact for IT security issues in Germany, helps to avoid risks faced by plant owners and operators. The BSI publication on cyber security provides an overview of the generic requirements for industrial remote maintenance according to the current state-of-the-art. The BSI recommends the use of a uniform solution and the location of the remote maintenance component in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) as well as the use of dedicated systems for remote maintenance. Connections are always established from the inside to the outside. The granularity of the accounts and strong authentication mechanisms are further criteria for a secure remote maintenance solution. Besides secure protocols, secure cryptographic procedures must be used. Other points listed by the BSI relate to password security, attack detection, risk analysis and the principle of minimalism.
What Does the Secure Remote Access Solution from HIMA and genua Do?
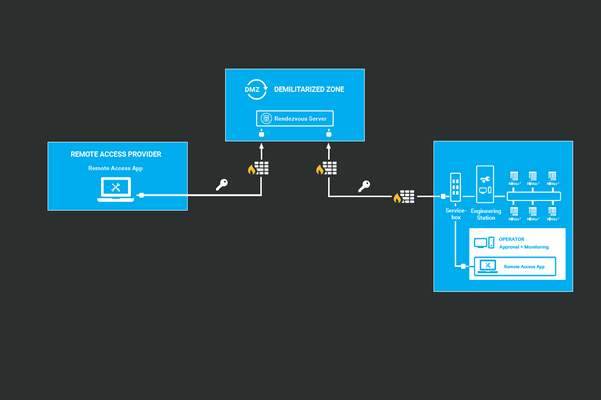
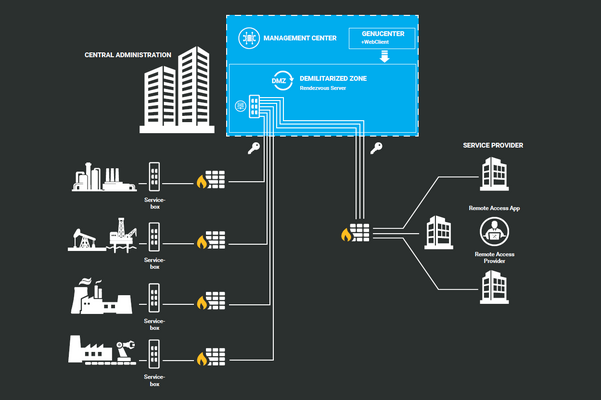
The uniform secure remote access solution from HIMA and genua complies with the BSI recommendations. It provides a uniform application for all remote maintenance cases and also enables a central management solution. Using a single solution also reduces complexity, another major customer benefit. A dedicated server is implemented as a central remote maintenance gateway in the DMZ, thus ensuring full control through an upstream DMZ. With the Rendezvous solution, no unilateral access from the remote maintenance service to the customer network is permitted. Instead, all maintenance connections run via a Rendezvous server installed in a DMZ, where both the maintenance service and the customer establish connections in an agreed time window.
The Rendezvous server establishes and maintains the continuous maintenance connection. Service engineers can now access the local engineering environment, which is segregated from the rest of the customer network by the remote maintenance app. The machine operator can also monitor the remote maintenance channel using the dual control principle.
As required by the BSI, the new remote maintenance solution also enables attack detection by identifying any failed authentication attempts. All remote maintenance access attempts are fully monitored and recorded for inventory purposes. The time window for remote accesses can also be restricted as required. Interactions can be tracked via central monitoring, with the added benefits of central patch management, logging and alerting.
An important consideration for users is also the investment security through IPv6 support and continuous product maintenance. Another positive aspect is that the HIMA remote maintenance solution is not limited by proprietary solutions. The highly secure remote maintenance solution enables comprehensive support of processes and user roles. It is easily scalable through central management, even for large environments – a further economic advantage for the user.
Conclusion
The high-availability remote maintenance solution presented by HIMA und genua complies with BSI recommendations and fulfils the highest safety and security requirements. Users can integrate the solution seamlessly in the HIMA Smart Safety Platform concept. HIMA customers will therefore benefit from significant advantages when using the remote maintenance solution presented, while effectively covering all central security risks.
Author: Alexandre Terentiev, DCS Expert – TÜV Functional Safety Engineer, SIS at HIMA Group