A new generation of pellet plants featuring a circular induration furnace as its core element was developed by Siemens Metals Technologies. It is referred to as Circular Pelletizing Technology (CPT).
Circular Pelletizing Technology (CPT) is an iron ore agglomeration facility characterized by its highly compact layout and light-weight construction design. This is the basis for efficient and cost-effective installation at a mining site or within an iron and steel complex. Pellet production capacities range from 800,000 t/a up to three million t/a and the quality of the pellets can be flexibly adjusted according to production requirements.
The ever-higher portion of fine and ultrafine iron ore from mining sites means that the pelletizing process is becoming more important for ore agglomeration. This has led to an increased interest by steel producers to invest in their own pellet plants to become independent of escalating prices for pellets on the global market. Up until now, however, space requirements and high investment costs for a conventional plant generally precluded its installation within an existing steelworks.
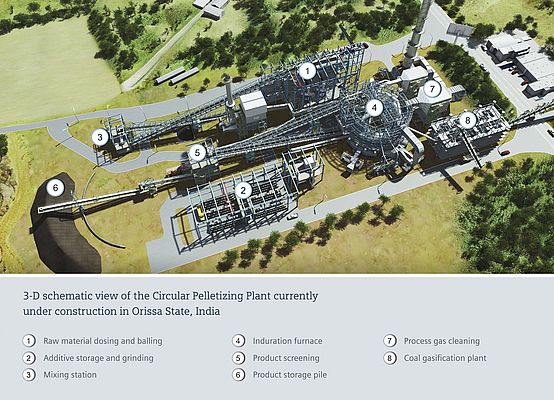
As an answer to this situation and simultaneously to reduce the capital expenditures for new facilities, Siemens Metals Technologies recently developed Circular Pelletizing Technology. This solution is based on the well-proven travelling-grate pelletizing process, however, the circularly designed induration furnace greatly reduces the footprint of the pelletizing plant. Overall space requirements for CPT are approximately one half of those needed for a conventional pellet plant. Costs for civil works, equipment and steel structure are reduced accordingly and plant installation can be completed far more quickly. The circular induration furnace also results in a more efficient utilization of installed equipment because nearly twice the number of pallet cars are always inside of the induration furnace compared to a straight-type induration furnace of the same capacity.
The intelligent and maximized reuse of hot gases minimizes the energy consumption required for pelletizing and, in combination with total recycling loops for waste materials and even steel mill reverts, a low environmental impact is ensured by the process. The installation of CPT within a steelworks not only allows producers to become independent of erratic prices for commercially available pellets, the chemistry and quality of the pellets can also be flexibly adjusted to meet the requirements of blast furnaces or direct-reduction plants.
The world's first CPT plant is currently under construction in Orissa State, India. Total space requirements for the complete facility, which extends from raw material dosing and balling to process gas cleaning and which also includes a coal-gasification plant to generate burner fuel, is less than two hectares. Start-up is scheduled for the second half of 2013 after which the plant will be capable of producing 1.2 million tons of pellets per year for the Indian iron and steel industry.